What is Financial Risk? Understanding Financial Risk in Malaysia (2025)

When talking about finance in Malaysia, one question often arises: What is financial risk? In simple terms, financial risk is the possibility of losing money or facing uncertain outcomes in financial decisions.
In Malaysia, financial risk is not just a textbook concept. It is a real challenge that affects businesses, investors, and households especially in 2025, with current issues like export tariffs, rising debt, and ongoing financial scandals.
What is Financial Risk in Malaysia?

Financial risk refers to the chance that actual financial results turn out worse than expected. This could mean:
- Businesses losing profit due to weak markets.
- Investors facing losses from stock or currency volatility.
- Households struggling with debt repayments during economic stress.
In the Malaysian context, financial risk is influenced by both global events (like U.S. tariffs and EU regulations) and domestic issues (like fiscal deficits and the Ringgit’s performance).
Types of Financial Risk in Malaysia (with Current Issues)
1. Market Risk – U.S. Tariffs on Malaysian Exports
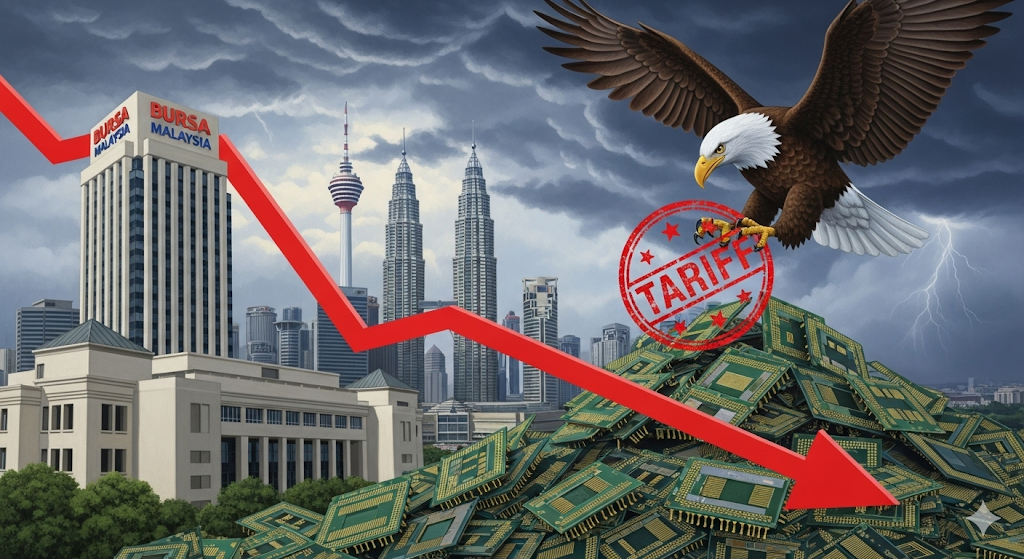
Malaysia’s reliance on semiconductor exports faces serious market risk. In 2025, the U.S. imposed a 19% tariff on Malaysian products, with potential hikes up to 100%. This impacts exporters, Bursa Malaysia-listed companies, and overall economic growth.
👉 Investors should watch trade news closely and diversify their portfolios to manage market risk.
2. Regulatory & Environmental Risk – EU Deforestation Law
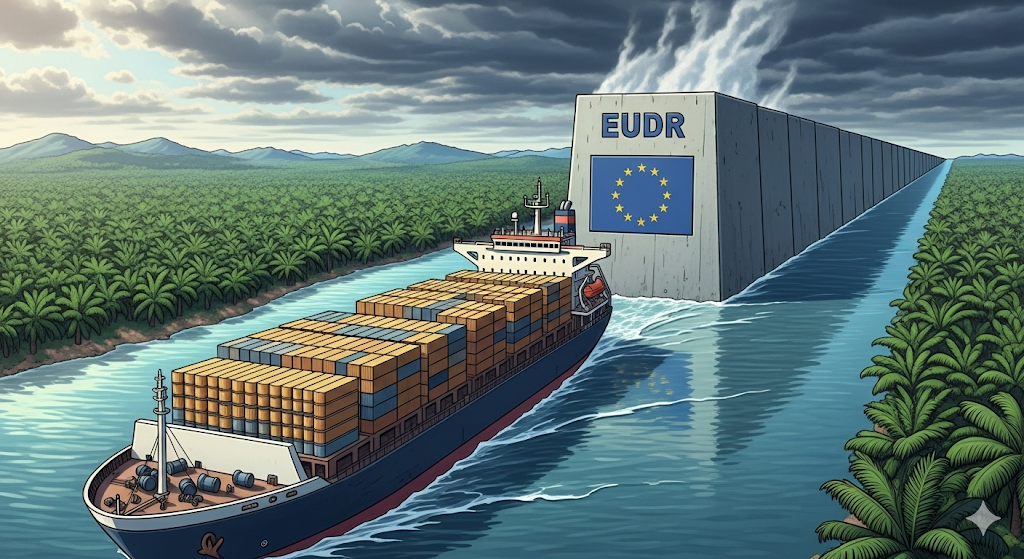

The new EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) affects Malaysian palm oil exports. Starting December 2025, shipments face stricter compliance checks. This is a form of regulatory risk, where businesses must adapt to avoid revenue losses.
👉 Agriculture investors and exporters must prepare ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) strategies to stay competitive.
3. Institutional Risk – 1MDB Scandal Fallout

Malaysia’s financial credibility still faces institutional risk due to the 1MDB scandal. These scandals remind Malaysians that weak governance can damage investor confidence and financial stability. The ongoing lawsuits and global settlements highlight the importance of strong compliance, transparency, and regulatory enforcement in the financial sector. Without these safeguards, Malaysia risks higher borrowing costs, reduced foreign direct investment (FDI), and long-term reputational damage in global markets.
4. Fiscal & Sovereign Risk – Rising Debt Levels
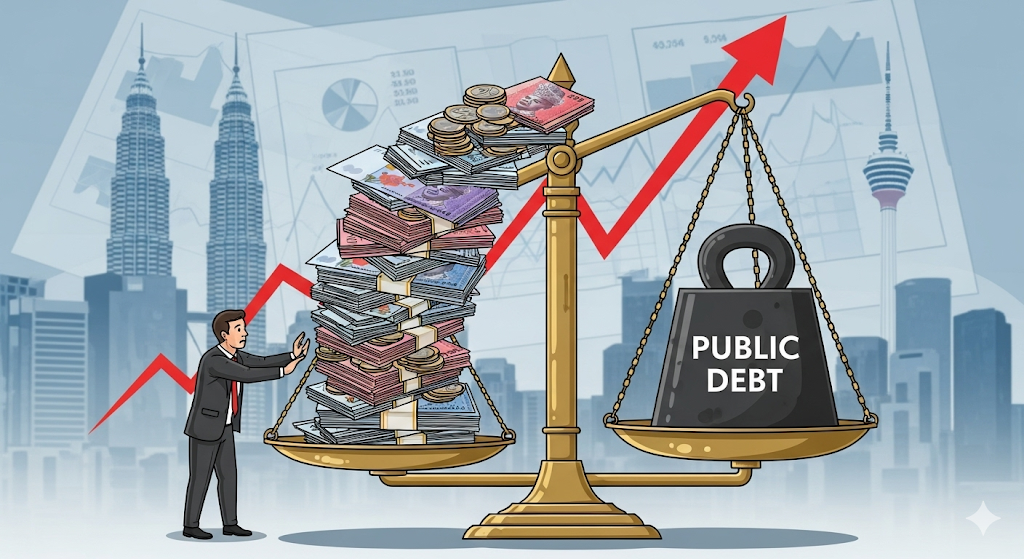
Malaysia’s public debt hovers around 68–70% of GDP, putting pressure on government finances. With subsidy costs and slow reforms, fiscal risk is high. If not managed well, this could affect Malaysia’s credit rating and increase borrowing costs.
👉 Businesses and investors should monitor government fiscal policies and Bank Negara Malaysia’s monetary moves.
5. Currency & Household Risk – Ringgit Weakness and High Debt
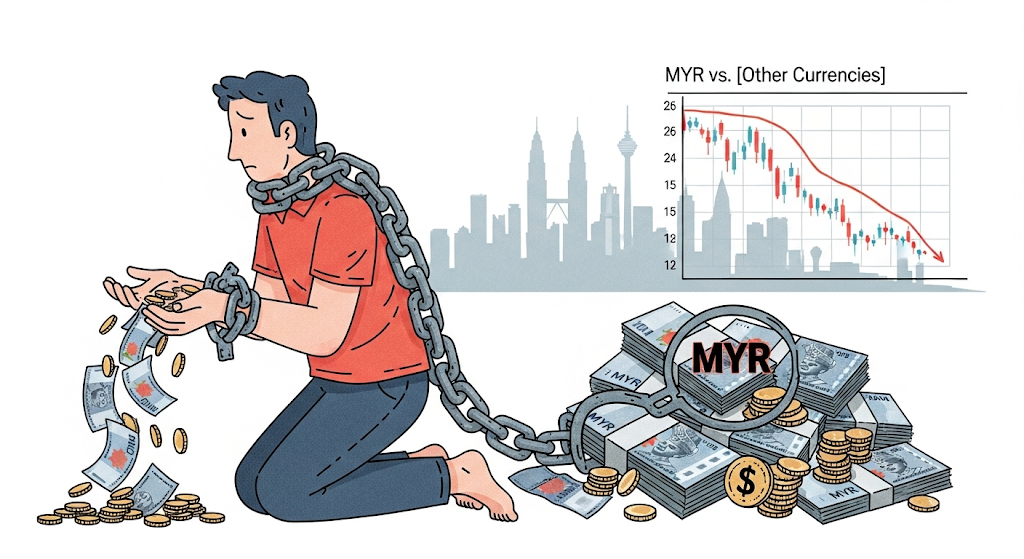
The Ringgit (MYR) continues to weaken against major currencies, exposing Malaysians to currency risk. At the same time, household debt is at 81–85% of GDP, one of the highest in Asia. This makes families vulnerable to interest rate changes and inflation.
👉 Individuals can manage risk by reducing unnecessary debt, building emergency savings, and diversifying income sources.
6. Climate & Transition Risk – Nature-Linked Financing

According to the World Bank, 87% of Malaysian bank lending is tied to sectors vulnerable to climate and ecosystem risks. This climate-related financial risk could impact both banks and borrowers if not managed carefully.
Why Financial Risk Matters in Malaysia

Financial risk impacts every layer of the economy:
- Investors need to protect portfolios from volatility.
- Businesses must prepare for global trade and regulatory shifts.
- Individuals must manage personal debt and inflation risks.
By understanding these risks, Malaysians can make smarter financial decisions.
How Malaysians Can Manage Financial Risk

- Diversify investments across stocks, bonds, gold, and real estate.
- Monitor Bank Negara Malaysia’s policies on interest rates and inflation.
- Adopt strong ESG practices for businesses exposed to global regulations.
- Strengthen personal finance discipline to reduce household debt stress.
Final Thoughts
In 2025, financial risk in Malaysia is shaped by global trade tensions, environmental regulations, legacy scandals, fiscal pressure, and climate concerns. While risks cannot be avoided, they can be managed with knowledge, planning, and diversification.
Understanding financial risk today is the first step toward building a stronger financial future for Malaysians.

